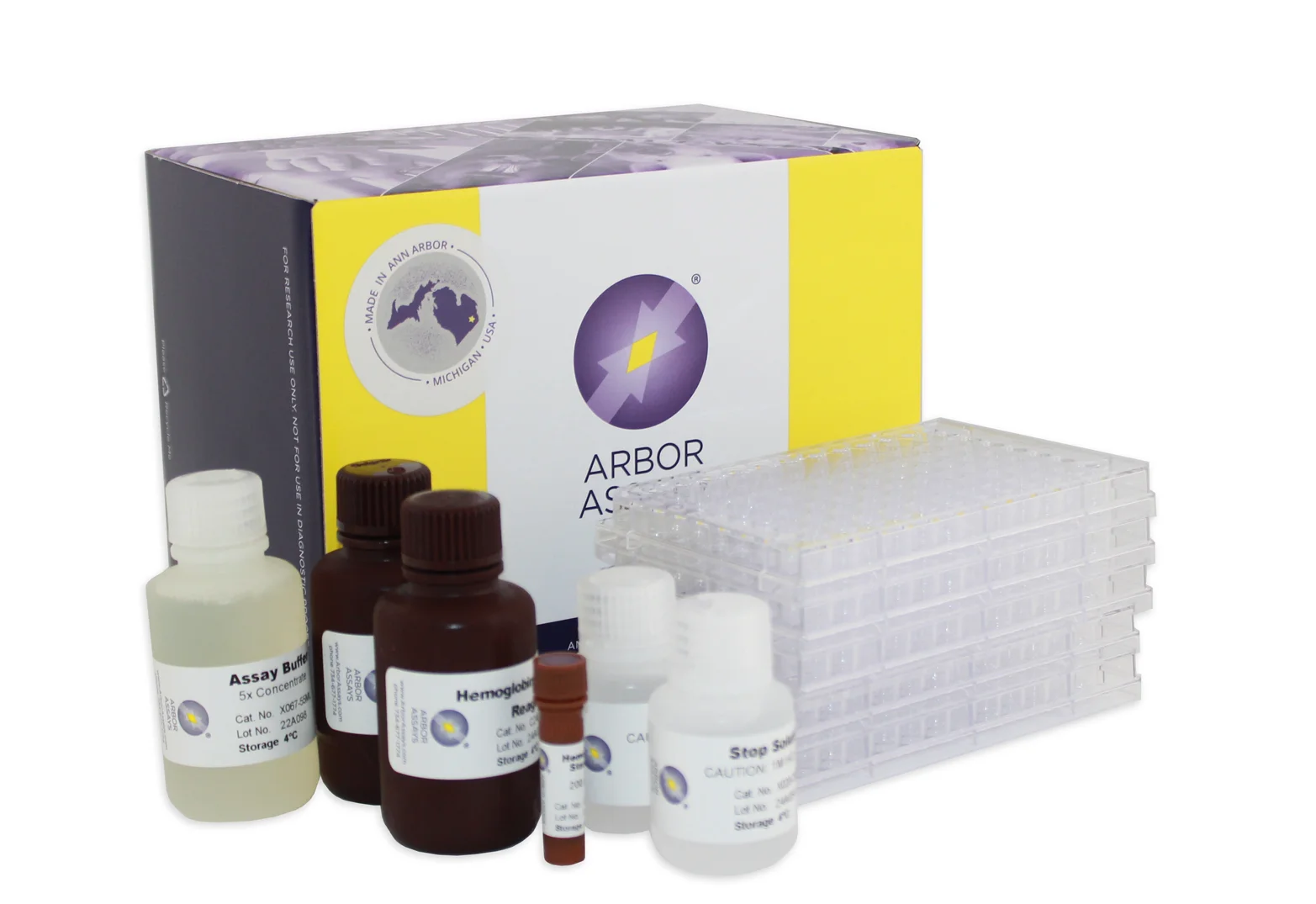
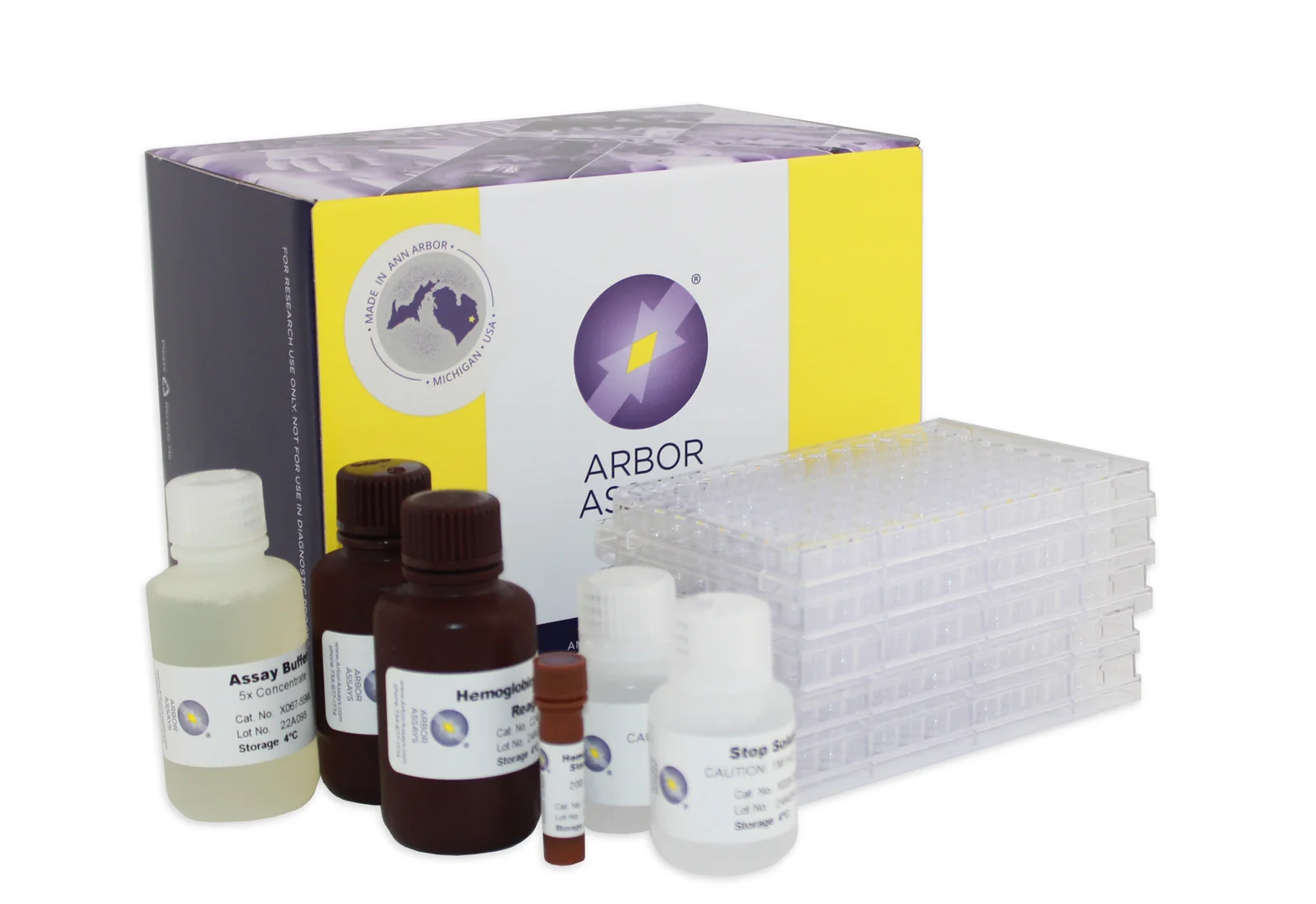
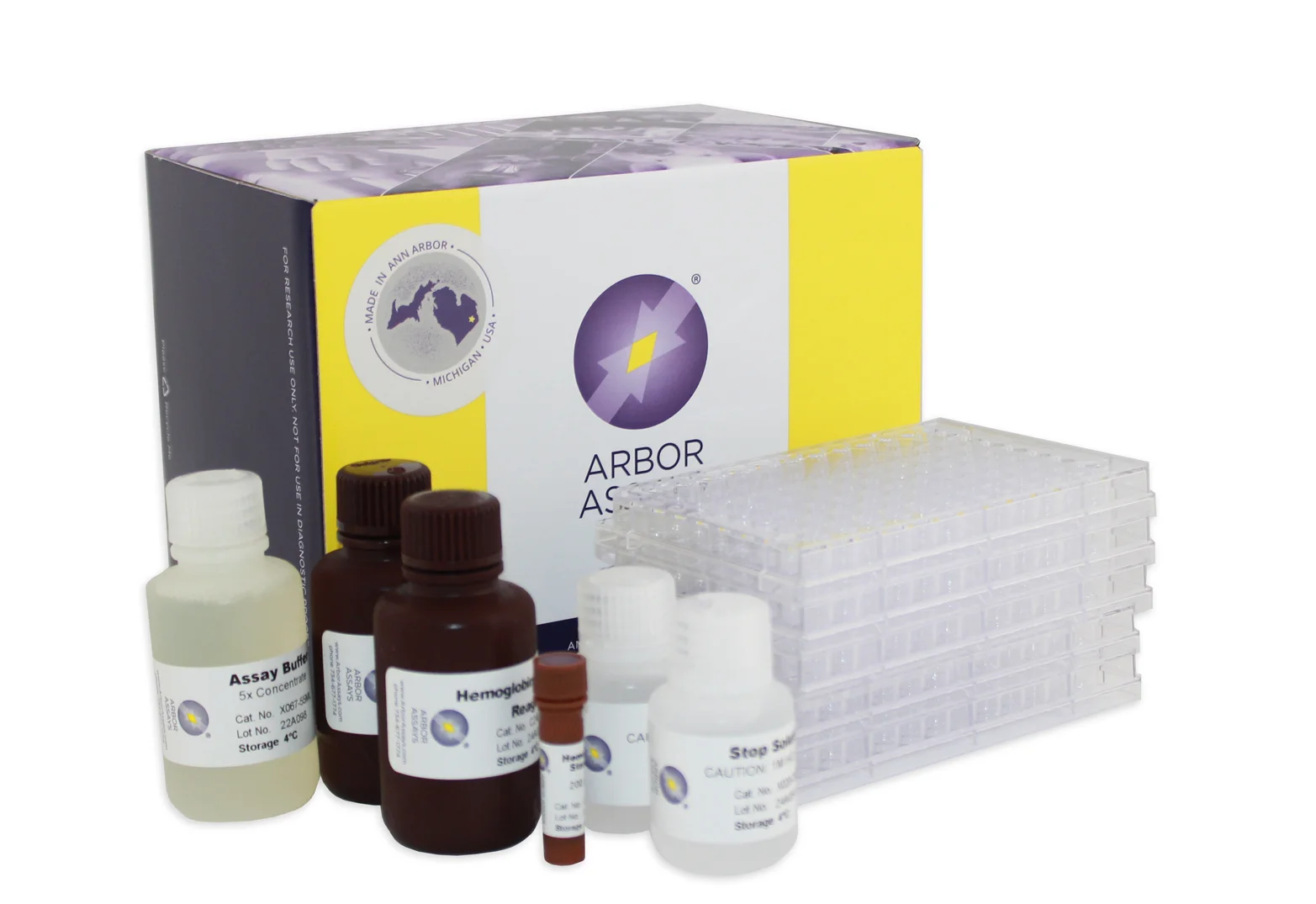
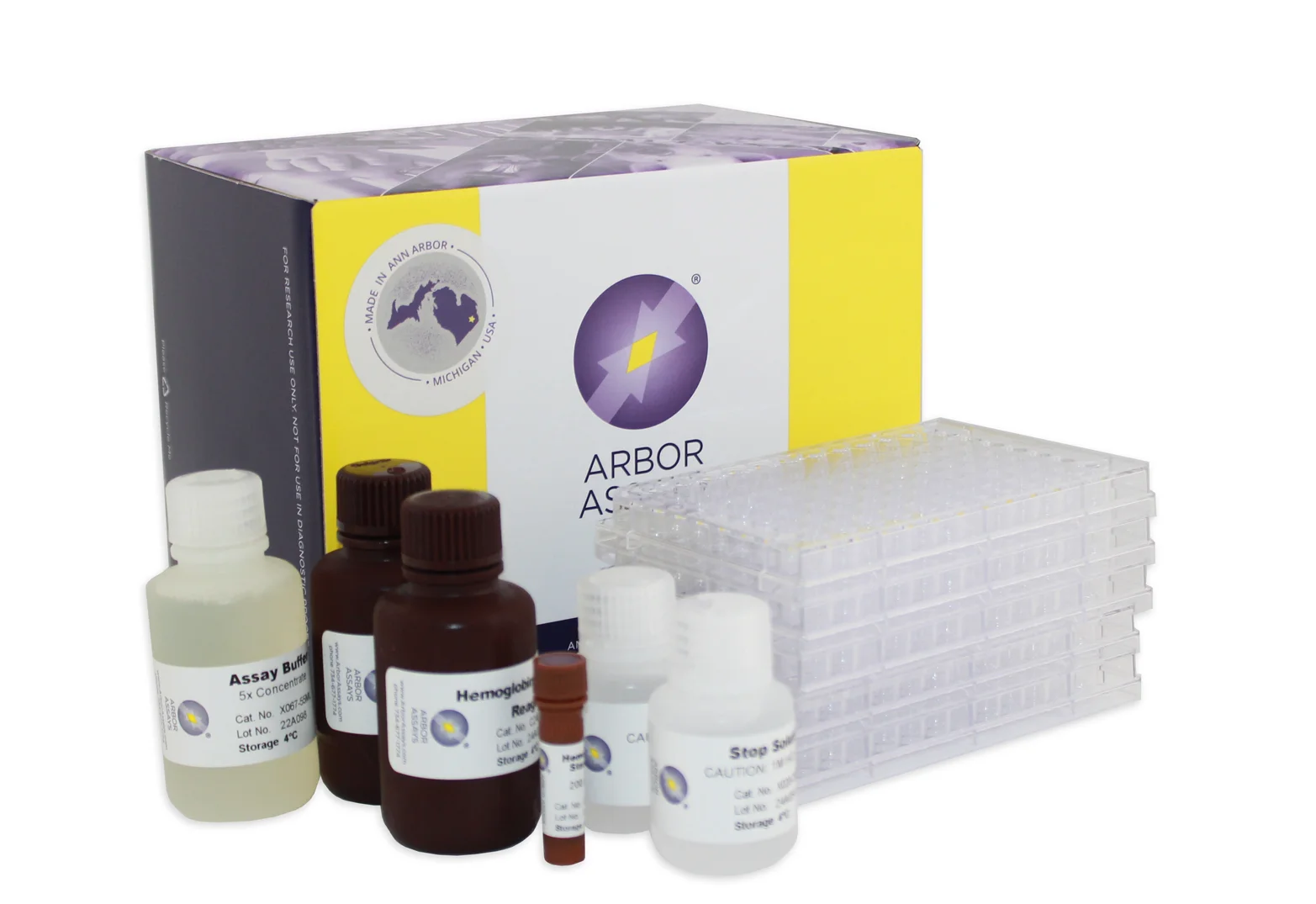
Arbor Assays ELISA Kits
Arbor Assays ELISA Kits
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
The neuropeptides, oxytocin and vasopressin, were isolated and synthesized by Vincent du Vigneaud at Cornel Medical College in 1953, work for which he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 19551. The neurohypophysial hormone arginine vasopressin (AVP), which is also known as an antidiuretic hormone, is involved in a wide range of physiological regulatory processes, including renal water reabsorption, cardiovascular homeostasis, hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary, and modulation of social behavior and emotional status2.
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
The neuropeptides, oxytocin and vasopressin, were isolated and synthesized by Vincent du Vigneaud at Cornel Medical College in 1953, work for which he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 19551. The neurohypophysial hormone arginine vasopressin (AVP), which is also known as an antidiuretic hormone, is involved in a wide range of physiological regulatory processes, including renal water reabsorption, cardiovascular homeostasis, hormone secretion from the anterior pituitary, and modulation of social behavior and emotional status2
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
Androstenedione is a steroid hormone also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione. It is synthesized from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) or 17-hydroxyprogesterone1. By itself, androstenedione is a weak androgen though it is a precursor for biosynthesis of stronger androgens, such as testosterone and estrogens. Therefore, androstenedione is classified as a controlled drug and a supplement to enhance athletic performance and body energy.
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
Allopregnanolone (3α-hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one) is a neurosteroid present in the blood and the brain. Allopregnanolone is made from progesterone which is converted into 5α-dihydroprogesterone by 5α-reductase type I. 3α-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase isoenzymes convert this intermediate into allopregnanolone. 3α-hydroxysteroids do not interact with classical intracellular steroid receptors but bind stereoselectively and with high affinity to receptors for the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in brain, g-amino-butyric acid (GABA)1. While allopregnanolone, like other GABAA receptor active neurosteroids, such as allotetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone, positively modulates all GABAA receptor isoforms, those isoforms containing δ-subunits exhibit greater magnitude potentiation.
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
Aldosterone, C21H28O5, is a mineralocorticoid first isolated by the husband and wife team of Simpson and Tait at University College, London in 19531. Initially called electrocortin, 21mg was isolated from 500 kg of beef adrenal glands. Aldosterone controls the sodium-potassium balance through the unidirectional salt reabsorption in a variety of tissues and glands2,3. Synthesized from cholesterol in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex, secretion is regulated through the renin-angiotensin system4 . Angiotensin II and potassium stimulate primary secretion by increasing the rate of production of the steroid.
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
Aldosterone, C21H28O5, is a mineralocorticoid first isolated by the husband and wife team of Simpson and Tait at University College, London in 19531. Initially called electrocortin, 21mg was isolated from 500 kg of beef adrenal glands. Aldosterone controls the sodium-potassium balance through the unidirectional salt reabsorption in a variety of tissues and glands2,3. Synthesized from cholesterol in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex, secretion is regulated through the renin-angiotensin system4. Angiotensin II and potassium stimulate primary secretion by increasing the rate of production of the steroid.
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH, also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a 39 amino acid polypeptide hormone (MW=4,500) secreted by the pituitary to regulate the production of steroid hormones by the zona fasciculata region of the adrenal cortex. ACTH is an important component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA) produced in response to biological stress. Its principal effects are increased production and release of glucocorticoids (GCs).
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
Cyclic dinucleotides are the most abundant second messenger in bacteria, modulating a variety of cellular activities in prokaryotic cells. 3’3’-cyclic GAMP (cyclic [G(3’,5’)pA(3’,5’)p], previously known as cGAMP) is a key mediator of bacterial signal transduction and regulation, controlling a range of diverse targets including transcription, enzyme activity and cell cycle progression. 3’3’-cGAMP signaling in bacteria is regulated in-part by gene regulatory RNA elements called riboswitches that bind and respond to cGAMP with high affinity and specificity1. The 3’3’-cGAMP riboswitches regulate genes involved in motility, biofilm formation, colonization, and virulence2, 3. The cyclic dinucleotides have emerged as key central regulators of bacterial physiology and inhibition studies of cGAMP signaling as an anti-microbial strategy are ongoing.
Manufacturer: Arbor Assays
The first insect molting hormone was isolated from silkworm pupae and determined to be a steroid, so named ecdysone, in 19541. Later, 20-hydroxyecdysone was identified in crayfish and recognized as a derivative of ecdysone2. These molecules and related forms are a family of steroid hormones that regulate metamorphosis, cell death, reproduction in arthropods, and are widely distributed in plant species(phytoecdysteroids)3. Of the many ecdysteroids, 20-hydroxyecdysone is the most functionally active and widely distributed in arthropods4. To accommodate growth during all immature stages of insects and other arthropods, 20-hydroxyecdysone levels change and activate signaling through an ecdysone receptor that results in the synthesis of a new exoskeleton and ecdysis of the old cuticle4,5. In female mosquitoes and flies, 20-hydroxyecdysone regulates egg development5.