
Influx
Estradiol, a form of estrogen, is a critical hormone in both the male and female bodies, playing vital roles in reproductive health, bone density, and overall well-being. This steroid hormone is primarily produced in the ovaries in women, but it is also synthesized in smaller amounts in the testes of men and in the adrenal glands of both sexes. Understanding estradiol's functions, regulation, and implications for health is essential for recognizing its impact on human physiology.
.jpeg)
What's Estradiol all about?
Estradiol (E2) is one of the three primary estrogens, the others being estrone (E1) and estriol (E3). It is the most potent form of estrogen and is involved in various physiological processes. Estradiol is synthesized from cholesterol and is classified as a steroid hormone. Its structure allows it to easily pass through cell membranes and bind to estrogen receptors, exerting its effects at both genomic and non-genomic levels.
Production and Regulation:
In women, estradiol is predominantly produced in the ovaries, particularly in the granulosa cells of the ovarian follicles. The production is regulated by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland through the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. The process begins with the hypothalamus releasing gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones promote ovarian follicle development and stimulate estradiol production.
.jpeg)
In men, estradiol is produced in the testes through the conversion of testosterone by the enzyme aromatase. The balance of estradiol and testosterone is crucial for various male reproductive functions and overall health.
.jpeg)
Functions of Estradiol:
1. Reproductive Health: Estradiol is integral to the menstrual cycle in women. It plays a crucial role in follicular development, ovulation, and the maintenance of the uterine lining. During the menstrual cycle, estradiol levels rise, leading to ovulation and preparing the uterus for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. If pregnancy does not occur, estradiol levels decline, leading to menstruation.
.jpeg)
2. Bone Health: Estradiol has a significant impact on bone density. It helps regulate bone remodeling by inhibiting osteoclast activity (cells that break down bone) and promoting osteoblast activity (cells that build bone). This protective effect is especially important during menopause when estradiol levels drop, leading to an increased risk of osteoporosis.
.jpeg)
3. Cardiovascular Health: Estradiol contributes to cardiovascular health by promoting vasodilation, improving blood flow, and regulating cholesterol levels. It helps maintain the elasticity of blood vessels, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases.
.jpeg)
4. Metabolic Function: Estradiol influences body weight, fat distribution, and metabolism. It plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, impacting the risk of developing conditions like type 2 diabetes.
5. Mood and Cognitive Function: Estradiol affects neurotransmitter systems, influencing mood and cognitive function. Fluctuations in estradiol levels, particularly during the menstrual cycle or menopause, can affect mood stability and are linked to conditions such as premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and postpartum depression.

Estradiol and Menopause: As women approach menopause, typically occurring between ages 45 and 55, estradiol production declines significantly. This drop can lead to various symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness. The decrease in estradiol is also associated with increased risks of osteoporosis and cardiovascular diseases.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often used to alleviate menopausal symptoms and provide protective effects against osteoporosis. However, HRT must be approached cautiously, as it carries potential risks, including an increased risk of certain cancers and cardiovascular events.
Estradiol in Men:
While estradiol is often associated with women, it plays essential roles in men’s health as well. In men, balanced levels of estradiol are crucial for fertility, libido, and bone health. Low estradiol levels can lead to decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and increased body fat. Conversely, excessively high levels may be linked to gynecomastia (breast tissue enlargement) and other hormonal imbalances.
Measuring Estradiol Levels:
Estradiol levels can be measured through blood tests, usually as part of hormone panels assessing reproductive health. The normal range for estradiol varies based on age, sex, and menstrual cycle phase. In women, levels fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, peaking just before ovulation. In men, estradiol levels remain relatively stable but can vary due to factors such as body fat percentage and age.
Disorders Related to Estradiol Imbalance:
1. Hypoestrogenism: Low levels of estradiol, or hypoestrogenism, can result in symptoms such as hot flashes, irregular periods, infertility, and bone density loss. This condition is commonly observed during menopause or as a result of certain medical conditions or treatments (e.g., certain cancer treatments).
.jpeg)
2. Hyperestrogenism: Elevated levels of estradiol, or hyperestrogenism, can lead to issues such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and increased risk of certain cancers, including breast and uterine cancer. Environmental factors, such as exposure to endocrine disruptors, can also contribute to elevated estradiol levels.
Estradiol in Biotechnology Research:
Estradiol, a potent form of estrogen, plays crucial roles in various biological processes, making it an important molecule in biotechnology research. Its applications span multiple fields, including reproductive biology, cancer research, drug development, and environmental studies. This article explores the significance of estradiol in biotechnology and its various applications.
Role in Reproductive Biology:
1. Endocrine Disruption Studies: Estradiol is often used in studies investigating endocrine disruptors—substances that can interfere with hormone functions. Researchers assess how these chemicals impact estradiol signaling pathways and reproductive health, which is vital for understanding environmental health risks.
2. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): In ART, estradiol is used to stimulate ovarian function and prepare the endometrium for implantation. Research in this area focuses on optimizing hormone protocols to improve the success rates of procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Cancer Research:
1. Breast Cancer Studies: Estradiol is implicated in the development and progression of hormone-dependent cancers, particularly breast cancer. Researchers study its mechanisms of action, including how it promotes cell proliferation via estrogen receptors. Understanding these pathways can lead to targeted therapies and better treatment strategies.
2. Drug Development: Estradiol serves as a model compound for developing selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and aromatase inhibitors, which are used in treating breast cancer. Investigating estradiol's effects aids in designing drugs that modulate estrogenic activity with fewer side effects.
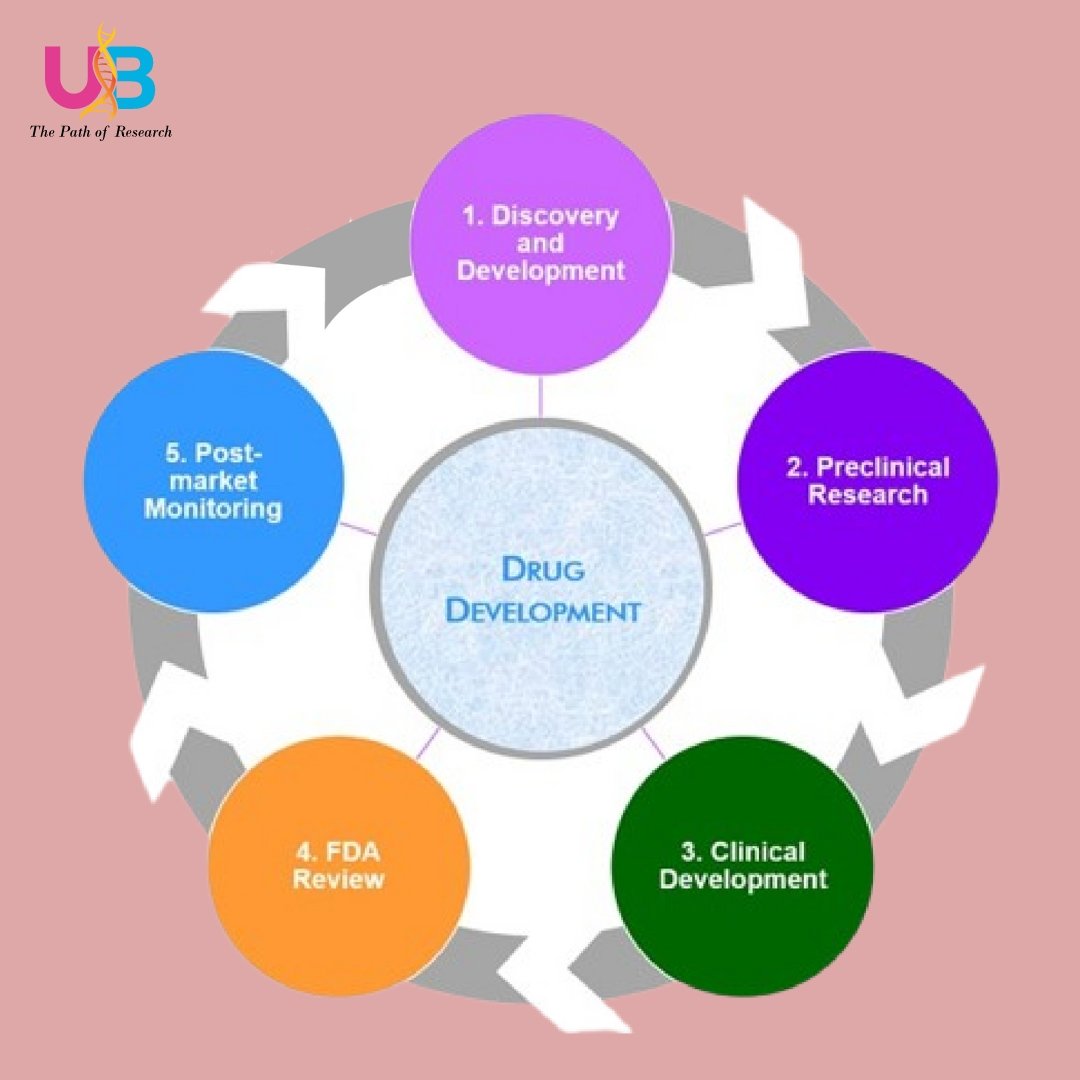
Metabolic Research:
1. Obesity and Diabetes: Estradiol’s influence on metabolism and fat distribution is a focus in obesity and diabetes research. Studies examine how estradiol levels affect insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism, contributing to the development of therapeutic strategies for metabolic disorders.
2. Bone Health: Given estradiol's role in bone density regulation, research investigates its application in treating osteoporosis. Biotechnological approaches aim to develop therapies that mimic or enhance estradiol's effects on bone metabolism.
Environmental Biotechnology:
1. Bioremediation: Estradiol and its analogs can be pollutants in water systems. Biotechnology research explores microbial degradation pathways for estradiol, aiming to develop bioremediation strategies to clean contaminated environments.
2. Ecotoxicology: Estradiol is used in ecotoxicological studies to assess the impact of pollutants on wildlife and ecosystems. Understanding its effects helps in formulating environmental policies and regulations.
Biomarker Development:
Estradiol levels serve as important biomarkers in various health conditions. Biotechnology researchers develop assays to measure estradiol in biological samples, which can aid in diagnosing hormonal imbalances, reproductive issues, and certain cancers.
Conclusion:
Estradiol is a vital hormone influencing various aspects of health, from reproductive functions to bone density and cardiovascular health. Understanding its roles and the effects of imbalances can help in the management of reproductive health and overall well-being. As research continues, the implications of estradiol in both women and men will likely yield new insights into treatment options and health strategies. For individuals experiencing symptoms related to estradiol imbalance, consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for appropriate evaluation and management.
Estradiol's multifaceted role in biotechnology research underscores its importance across various fields. From reproductive vigor to cancer therapy and environmental studies, ongoing research continues to uncover new applications and therapeutic potentials of this critical hormone. Understanding estradiol's mechanisms and impacts not only enhances scientific knowledge but also contributes to the development of innovative solutions in health and environmental management.
Examine the food safety kits from our renowned brand Elabscience to detect the Estradiol hormone residues samples. These tools are widely used in Government agencies (FDA, USDA, EFSA, EPA, NIH, CDC), scientific research units, health departments, nutrition and dietetics programs, scientific research arena, agricultural division, animal husbandry and environment health unit. We, Universal Biotechnology Private Ltd., is an Indian distributor for multiple overseas brands. We deal with ELISA kits, Assay kits, Antibodies, Recombinant proteins, Molecular Biology products, Custom Services, Benchtop equipment’s, Cell Culture products and Biochemicals related to research areas of Biotechnology, Bio-pharmaceutical, Pharmaceutical, Pathology labs, Food industry and Clinical trials in the nationwide to attain the demands of the research scholars. We offer high-quality Biotech research products from our renowned brands such as LabReCon, Abbkine, GeneTex, GeneDireX Inc., Fine Test, BT Laboratory, Arbor Assays, Cloud Clone Corporation, Affinity Biosciences, Pricella, GeneAll Biotechnology, ELK Biotechnology, DLAB Scientific, Gilson, UBTECH, Biomatik, Bioworld Technology, Reed Biotech, Unibio, ProSpec, Abbexa, Sunlong Biotech, Peak instruments Inc., Nippon Genetics and others. For inquiries and product assistance, connect with us via email at info@unibiotech.in or visit our website at www.unibiotech.in
